Explain Different Methods of Transfer Pricing
This is determined based on few widely accepted methods such as comparable uncontrolled price method cost plus pricing method resale price method Transactional Net margin method and transactional profit split method. The application of transfer pricing methods.
4 Types Of Pricing Methods Explained
Traditional transaction methods and transactional profit methods.
. The only condition that triggers transfer pricing is the existence of multiple facilities in more than one taxing jurisdiction. Transfer pricing methods 1. These two types of cost-based pricing are as follows.
User Friendly Computer Inc with headquarters in San Francisco manufactures and sells a en computer. Market-based transfer prices cost-based transfer prices and negotiated transfer prices. A transfer pricing method based on the comparison of the operating profit derived from related party transactions with the operating profit earned by third parties undertaking similar business activities.
When external markets do not exist or are not available to the company or. Market based transfer pricing. In cost-plus pricing method a fixed percentage also called mark-up percentage of the total cost as a profit is added to the total cost to set the price.
This methods involves transfer of goods at direct manufacturing cost incurred by the. The transaction between related enterprises for which an arms length price is to be established is referred to as the controlled transaction. A transfer price is based on market prices in charging another division subsidiary.
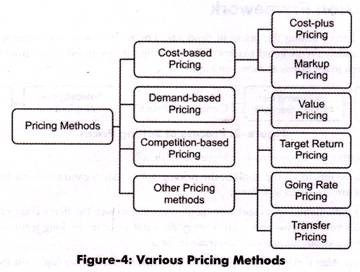
Manufacturing cost plus a predetermined mark up. The transfer of the goods and services should happen between. The three major categories of methods used to establish product prices are cost-oriented pricing competition-oriented pricing and demand-oriented pricing.
The CUP method is grouped by the OECD as a traditional transaction method. Entities under common control refer to those that are ultimately controlled by a. In some cases the transfer of goods and services from one.
Although each method provides a different answer their commonality is that transfer prices represent an intracompany market mechanism. Refers to the simplest method of determining the price of a product. User Friendly has three divisions each of which is located in a different country.
Transfer pricing disputes between taxpayers and tax authorities generally cover multiple financial years and can therefore substantially affect the financial position of a company. The five different methods of transfer pricing fall into two categories. 2 Cost Based Prices.
4 Arms-Length Transfer Pricing. Transfer pricing analyses equal to gross margin divided by operating expenses. Transfer pricing methods are ways of establishing arms length prices or profits from transactions between associated enterprises.
It is one of the reasons why globalisation has increased and why operating in more than one territory can be beneficial for firms looking to minimise their overall tax liability. The most common is cost-oriented pricing. Multinational transfer pricing effect of alternative transfer pricing methods global income tax iration.
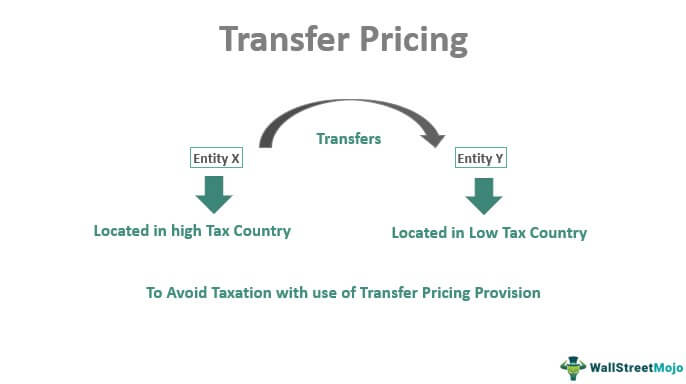
The price that would have been reached by unrelated parties in a similar transaction is referred to as arms-length transfer pricing. Transfer pricing is a method of pricing goods and services transferred within a multinational or trans-national company in order to reduce tax burdens and maximise profits. Transfer pricing accounting occurs when goods or services are exchanged between divisions of the same company.
Comparable uncontrolled price CUP method. A number of methods are prevailed for determination of the products price. Methods of Transfer Pricing 4 Methods 1 Market-Based Prices.
When transfer pricing occurs companies can book profits of goods and services in a different country that may have a lower tax rate. The concept of transfer pricing comes in place when goods are transferred from one unit to another especially when the two units are located in different countries. Transfer pricing refers to the prices of goods and services that are exchanged between companies under common control.
A retailer may use one or a combination of the methods. Length nature of prices or profits. Cost based transfer pricing.
An example is the deal that pharma giant AstraZeneca concluded with. For example if a subsidiary company sells goods or renders services to its holding company or a sister company the price charged is referred to as the transfer price. Another traditional transaction method for determining transfer pricing is the resale price.
The methods of transfer pricing can be divided into four categories. The method by which transfer prices are set is determined by management and can be any of the following broad systems. We will now discuss each type of transfer price.
For example a company with 45 employees in five locations in two states would activate transfer pricing concerns if one of its offices provides data processing payroll or other services to the others. Market price refers to a price in an intermediate market between independent buyers and. Comparable profits method CPM.
Generally companies can determine transfer prices three different ways. Methods of determining transfer price 1. This approach requires identifying an arms-length price which may be difficult.
This method is an improvement over direct manufacturing cost method.

Transfer Price Meaning Importance Example And More

Transfer Price Meaning Importance Example And More Transfer Pricing Accounting And Finance Economics Lessons
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Explain Different Methods of Transfer Pricing"
Posting Komentar